Finding
Among the 46 countries and Taiwan with nuclear facilities, support for new political and legal commitments and international assurances is faltering.
Data Highlights
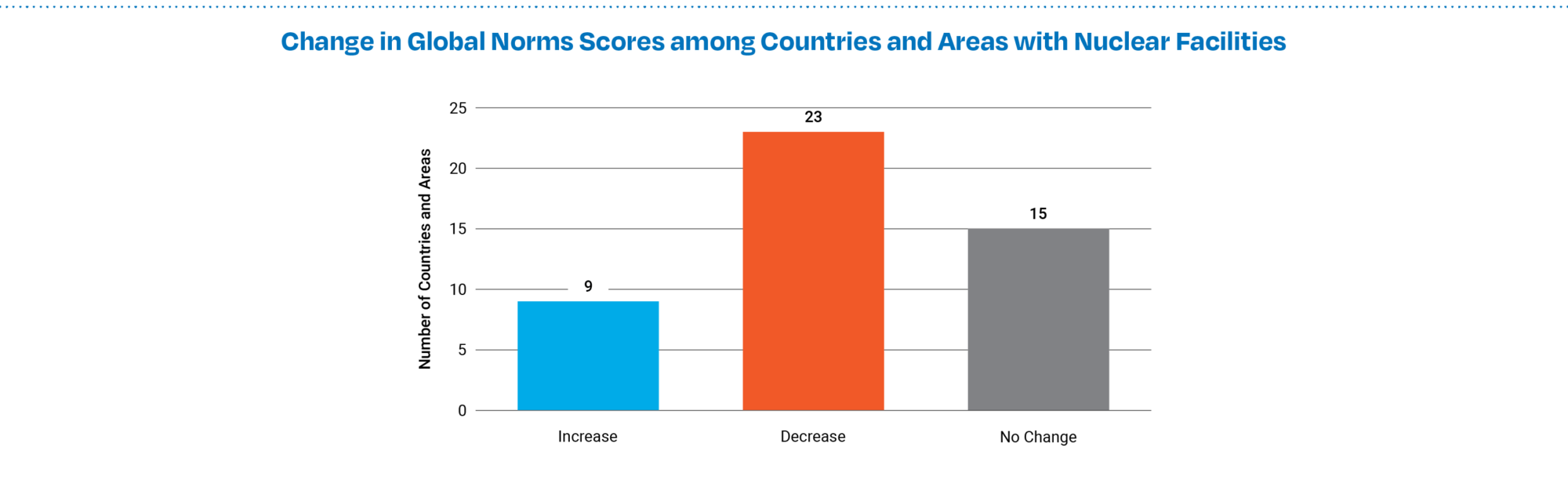
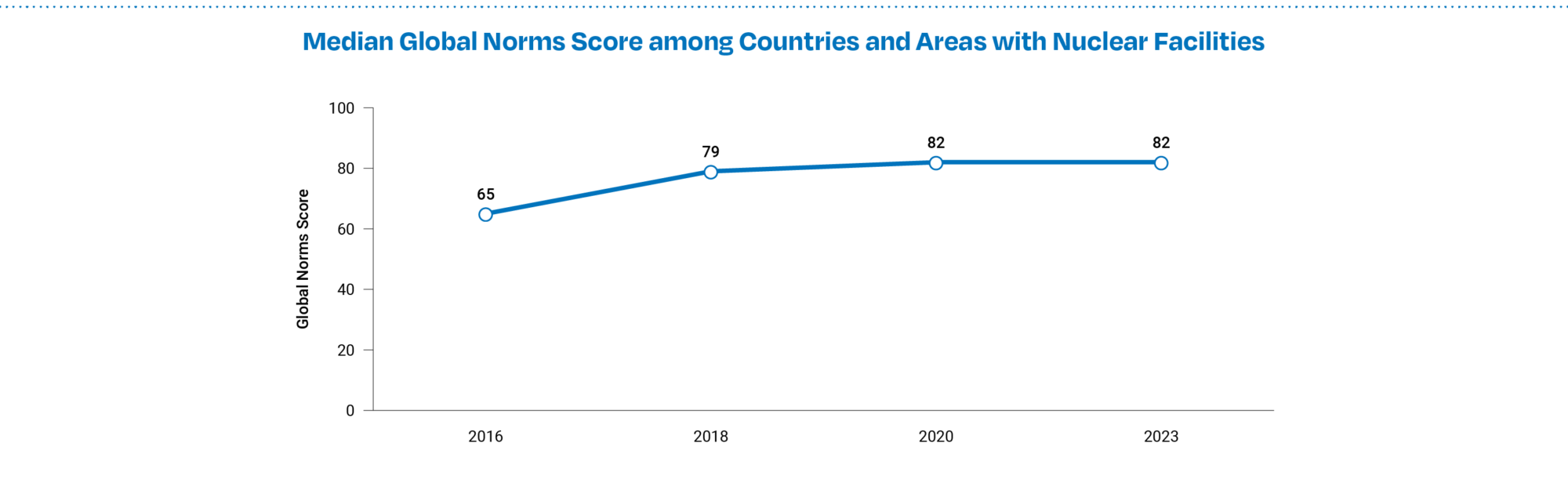
- Global Norms scores—which measure legal commitments, participation in international groups, and support for international organizations—decreased in 23 countries with nuclear facilities and increased in 9. This is the first time that the median Global Norms score among the 47 countries and areas with nuclear facilities did not increase. (See Figure 6a and 6b.)
- Brazil is the only country with nuclear facilities to join the amended Convention on the Physical Protection of Nuclear Material (CPPNM) since 2020. 4 countries with nuclear facilities—Egypt, Iran, North Korea, and South Africa—have not yet ratified the amendment.
- Slovenia and Switzerland are the only countries with nuclear facilities that made new political commitments to international nuclear security best practices since 2020. Both countries joined INFCIRC/908 on mitigating insider threats.
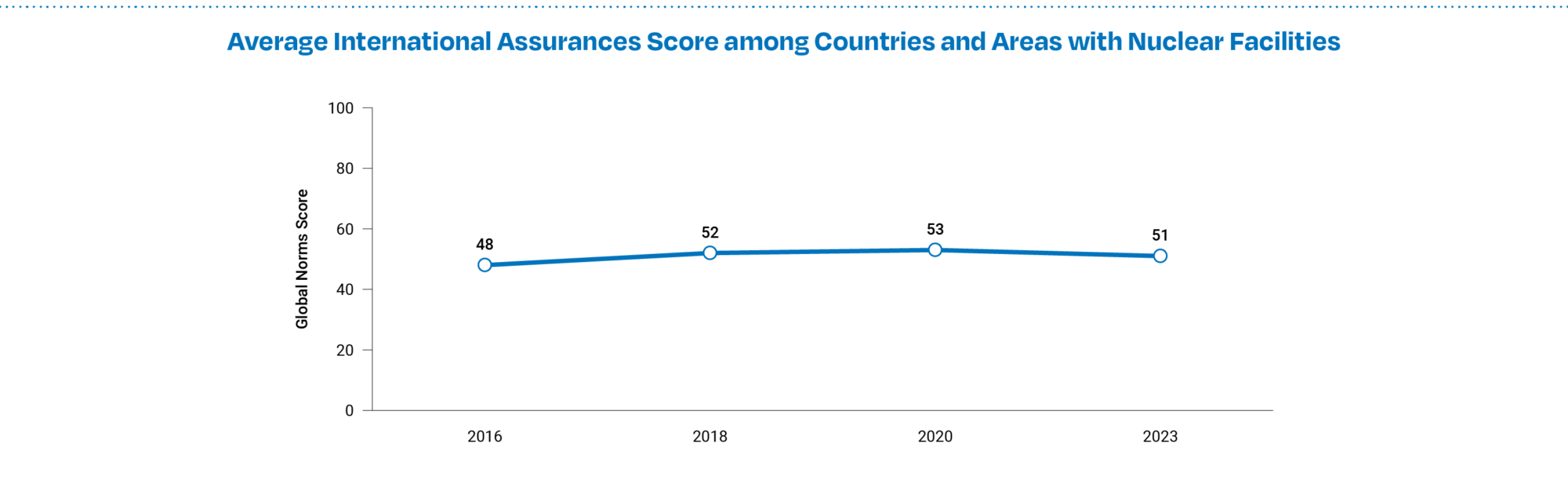
- International Assurances scores decreased for 21 countries with nuclear facilities and increased in only 7. This is the first time the NTI Index has measured a decrease in the average International Assurances score, which remains very low, for the 46 countries and Taiwan with nuclear facilities. (See Figure 6c.)
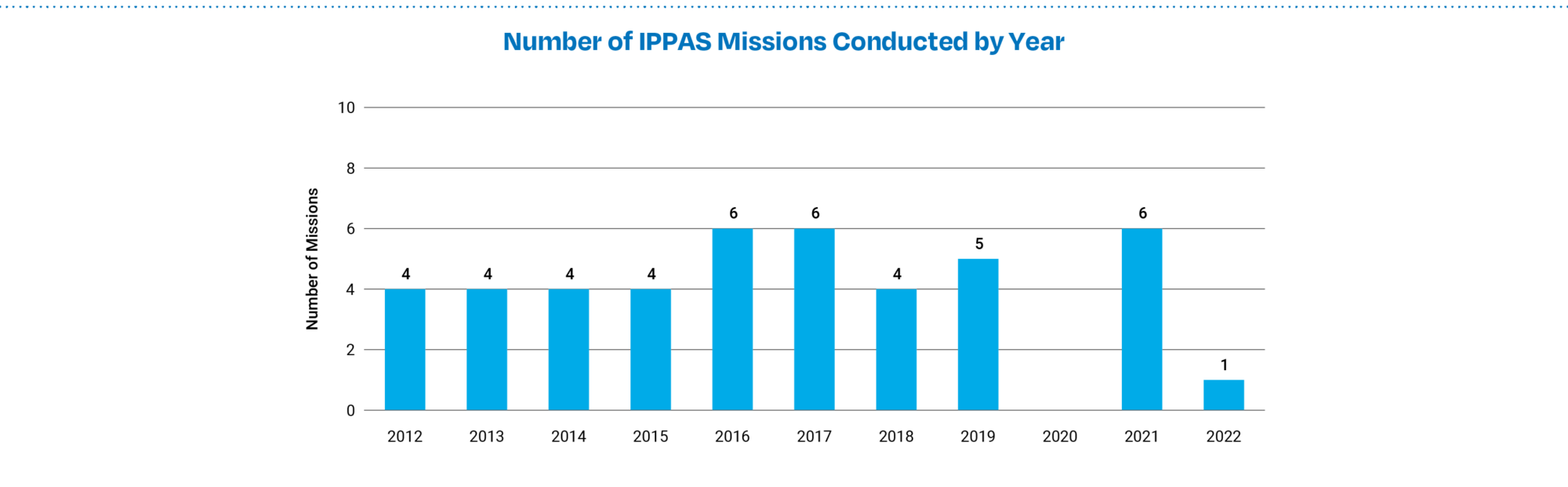
- As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, no countries or areas participated in International Atomic Energy Agency International Physical Protection Advisory Service (IPPAS) peer reviews in 2020. Finland is the only country that participated in an IPPAS mission in 2022. 5 missions are planned for 2023 (Bangladesh, Kuwait, the Netherlands, Romania, and Switzerland), a pace much closer to the historical high point of 6 annual missions. (See Figure 6d.)